Organic compounds are found all around us as they form the basis of many products that we use today. Read this ScienceStruck article to learn more about these compounds, and to see a brief list of the examples.
Any chemical compound that contains carbon molecules in its composition is an ‘organic compound’. There is even a special branch of chemistry (known as organic chemistry) that is solely dedicated to the study of these compounds. The distinction between organic and inorganic compounds is one that is shrouded with a bit of confusion as there are some carbonates, allotropes of carbon, and some cyanides that cannot be called organic even though they contain carbon molecules.
Now, an official definition of these compounds does not exist, and this makes the distinction process even harder. Different scientific books often give differing definitions. Some books state that these compounds contain C-H bonds, others state that they contain C-C bonds, and most books say that the simple presence of carbon makes a compound organic in nature.
Despite these differences, the examples remain the same in all these books. Once a compound has become known as an organic, this cannot be altered just like that.
What Are Organic Compounds Made Of?
The modern definition and classification of these examples are very different from earlier studies. Today’s fairly broad definition that any compound containing carbon qualifies as organic compounds is not completely accurate as there are several carbon-containing alloys that do not figure in this list.
Apart from these alloys (like steel), there are other metal carbonates and carbonyls, simple carbon halides and sulfides and simple oxides of carbon and cyanides as well, that are known as inorganic compounds, even though carbon is a part of their composition. The older definitions (known as ‘vitalism’) were considered by scientists to originate from living processes, and this led to the name ‘organic compounds’. The primary reason for so much ambiguity is that carbon easily combines with many compounds to form molecular chains and rings, and as such, there are millions of compounds that contain carbon in them.
Examples
The most commonly known and seen examples are as mentioned in the following list:
Alkanes
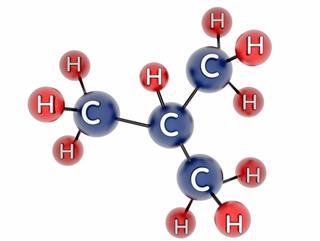
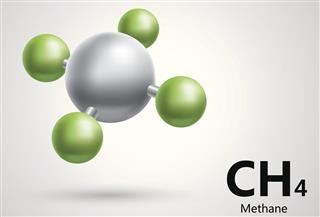
- Methane
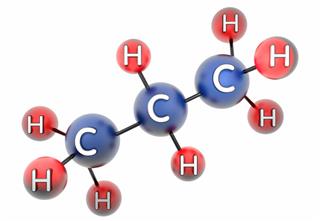
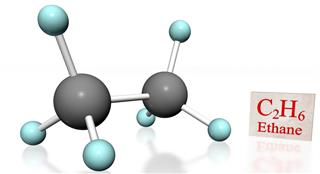
- Ethane
- Propane
- Butane
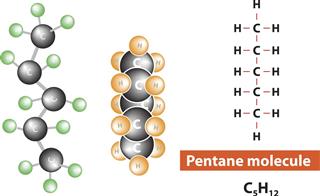
- Pentane
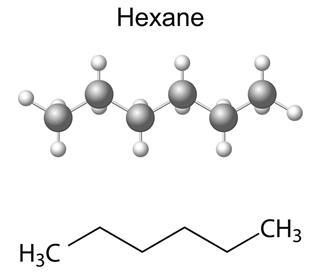
- Hexane
- Heptane
- Octane
- Nonane
- Decane
Cycloalkanes
- Cyclopropane
- Cyclobutane
- Cyclopentane
- Cyclohexane
- Cycloheptane
Some more Examples
- Acid anhydrides
- Acylhalides
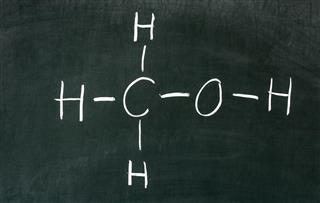
- Alcohols
- Aldehydes
- Alkenes
- Amides
- Amines
- Aromatics
- Azo compounds
- Carboxylic acids
- Esters
- Ethers
- Haloalkanes
- Imines
- Ketones
- Nitriles
- Nitro compounds
- Organometallic compounds
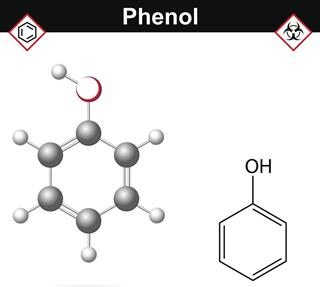
- Phenols
- Polymers
- Thiols
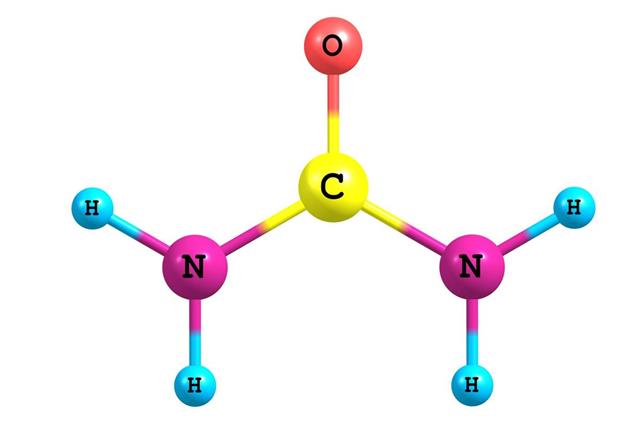
- Urea
- Valium
- Vitamins
- Warfarin
- Xylene
- Xylose
- Zingiberene
The wide use and application of organic compounds has made them very useful for the progress and development of mankind. These have a variety of applications in our everyday lives, and it would be impossible to imagine life without them. Apart from forming the basis for many applications and products that we use, these are also the main constituent of all forms of life.
These examples can be classified as natural and synthetic organic compounds, and also on the basis of the many bonds that they are made up of. The study of organic chemistry is very vast and complicated, but ultimately very useful.