Circuit diagrams provide the component layout in any circuit. In order to represent the various components used in the diagram, electrical symbols are used. Here’s a printable electrical symbols chart for your reference when preparing circuit diagrams.
Did You Know?
Edraw Max, an electrical diagramming program, was the first software to demonstrate standard electrical symbols on computer screens.
Electrical symbols are used to represent electrical and electronic devices in schematic diagrams. There are different country-specific standards, IEC (British), ANSI, and AS (Australian Standard), that define the symbols used in circuit diagrams across the world. However, today most of the symbols are internationally standardized. We have provided a list of the most commonly used electrical symbols in electrical drawings.
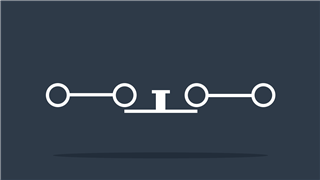
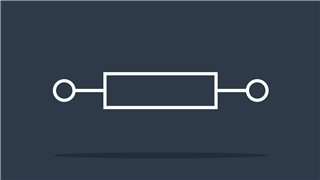
Wire
Passes electric current
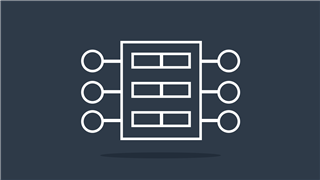
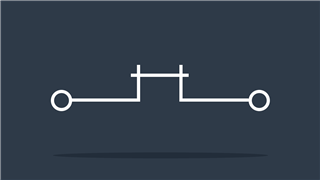
DIP
Manual on-off switch used on PCBs
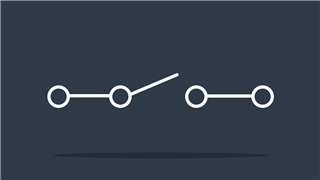
Single Pole, Single Throw (SPST) switch
An on-off switch which passes current in closed position
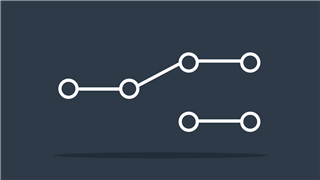
Single Pole, Double Throw (SPDT) switch
A changeover switch that directs current to one of the two available routes.
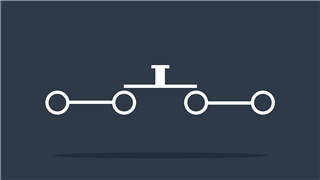
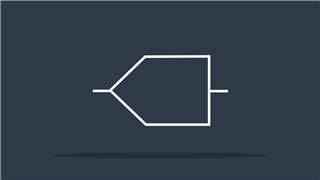
Pushbutton (NO)
Momentary switch that passes current when pressed
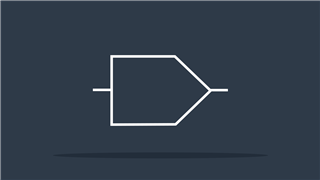
Pushbutton (NC)
Momentary switch that passes current when released
SPST Relay
On-off switch operated by electromagnet
SPDT Relay
Double throw switch operated by electromagnet
Jumper
Piece of wire that bypasses or closes onboard connections
Solder Bridge
Connection completed by soldering
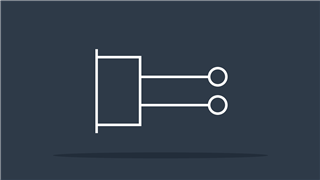
Ground
Connects to zero potential (or earth)
Chassis Ground
Connects the chassis of a device to zero (earth) potential
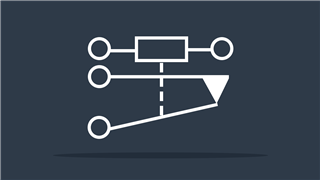
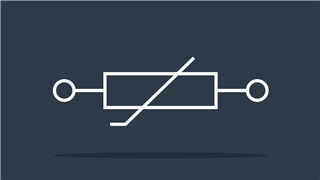
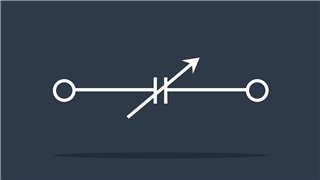
Resistor IEEE
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) standard symbol – Reduces flow of charge or current
Resistor IEC
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) symbol
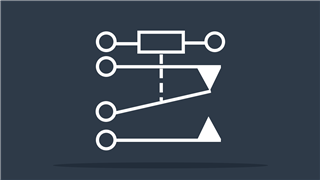
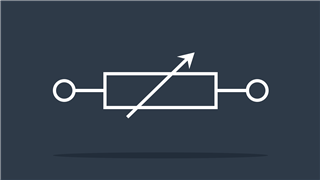
Potentiometer IEEE
IEEE symbol – Adjustable resistance value
Potentiometer IEC
IEC symbol
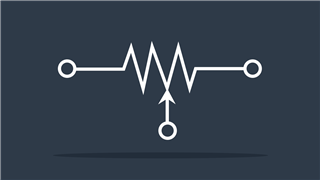
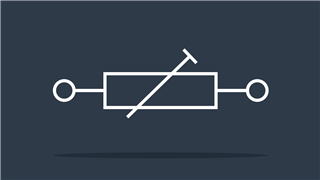
Rheostat IEEE
IEEE symbol – Variable resistance value
Rheostat IEC
IEC symbol
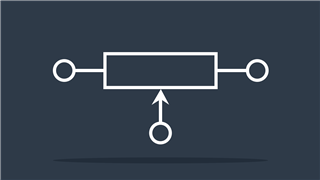
Trimmer
Adjustable resistor with preset value
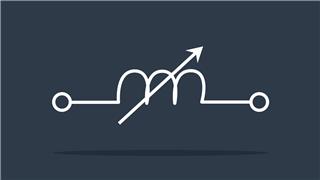
Thermistor
Resistance value changes due to changes in temperature
Capacitor
Stores electric current
Polarized Capacitor
Capacitors having electrolyte liquid in one of the plates
Variable Capacitor
Can change the value of capacitance
Inductor
Coil that generates magnetic field
Variable Inductor
Can adjust the value of inductance
Iron Core Inductor
Coil core contains iron
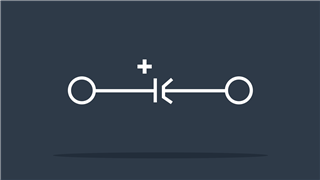
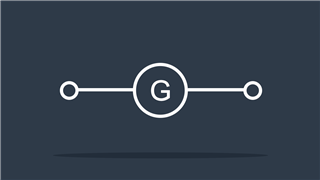
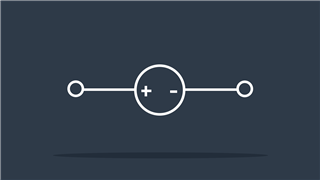
Generator
Generates electricity (voltage) by converting mechanical energy to electrical energy
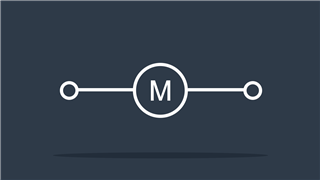
Motor
Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy
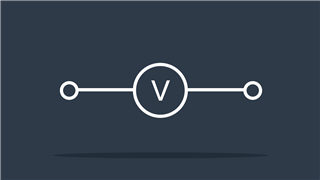
Voltmeter
Measures voltage
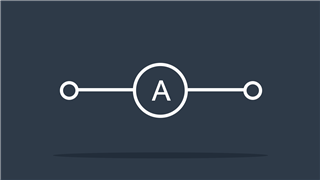
Ammeter
Measures current
Ohmmeter
Measures resistance
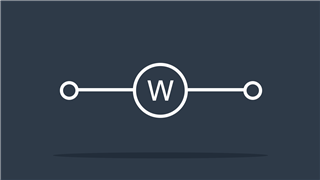
Wattmeter
Measures power
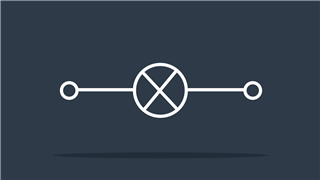
Lamp
Light source illuminated by current flow
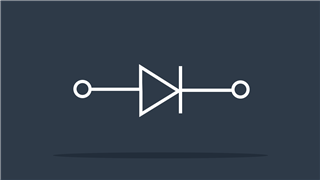
Diode
Allows current flow in only one direction
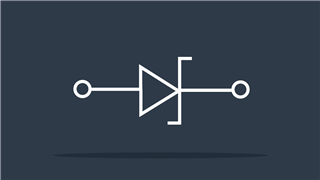
Zener Diode
Allows current flow in reverse direction only above breakdown voltage
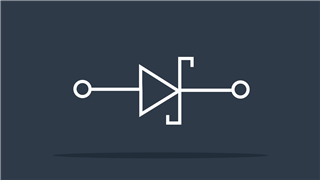
Schottky Diode
Diode with less voltage drop
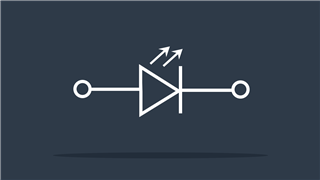
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
Emits light when current flows through
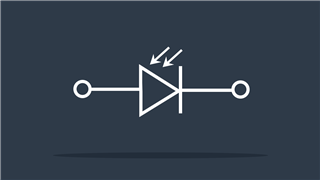
Photodiode
Allows current to flow only when exposed to light
NPN Bipolar Transistor
Current flows only when high potential applied to base
PNP Bipolar Transistor
Current flows only when low voltage applied to base
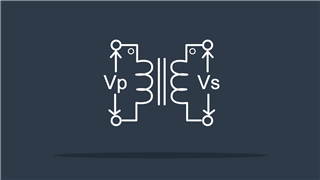
Transformer
Changes voltage from low to high value or vice-versa
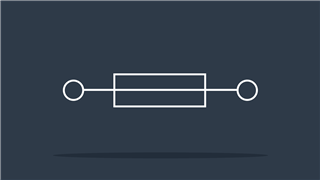
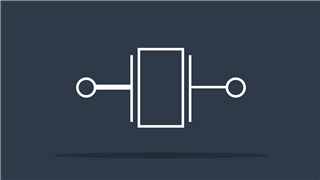
Fuse
Disconnects the circuit if current exceeds threshold value
Electric bell
Produces sound (ringing) when activated
Buzzer
Produces sound (buzzing) when current is applied
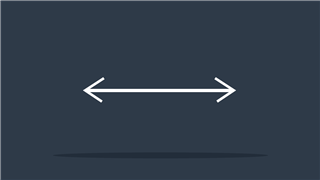
Bus
Collection of wires
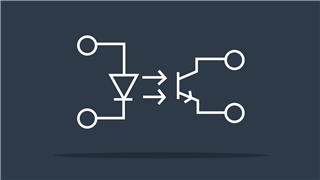
Optocoupler
Isolates two circuits on a single PCB
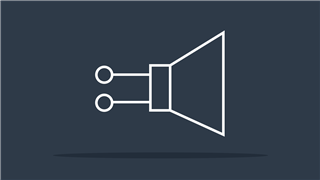
Loudspeaker
Converts electrical signal to sound waves
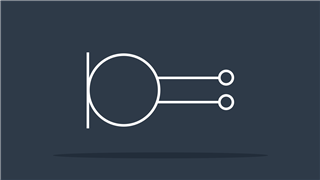
Microphone
Converts sound waves to electrical signals
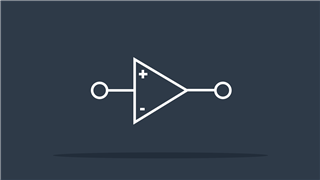
Operational Amplifier
Amplifies input signals
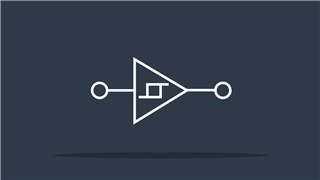
Schmitt Trigger
Removes noise from input signal
Analog-to-digital Converter
Converts analog signal to digital signal (numbers)
Digital-to-analog Converter
Converts digital signal to analog signal
Crystal Oscillator
Generates frequency clock signal
Antenna
Sends and receives radio waves
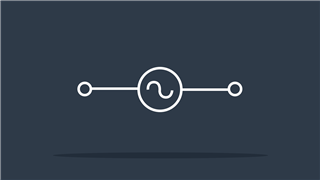
Alternating Current (AC)
Supplies current with continuously changing direction
Direct Current (DC)
Supplies current with constant direction
Circuit Breaker
Disconnects the circuit when current crosses threshold value
Earphone
Converts electrical energy to sound waves
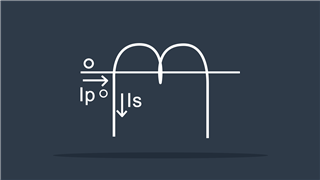
Current Transformer
Produces low current when input current is high
Voltage Transformer
Reduces voltage to lower level when it increases beyond safety limits